Heat as a Service (HaaS)
Heat as a Service (HaaS), a type of Energy as a Service (EaaS), is a third-party financing structure that allows industrial companies to implement innovative renewable heat solutions without the need for large upfront investments. Instead, companies pay for the consumed heat supplied by an independent energy service company (ESCO) which finances, builds, and operates the solution. The HaaS model can be used in combination with many different energy solutions including thermal energy storage, industrial heat pumps, and solar thermal technology. For example, the ESCO can install an industrial heat pump at the industrial offtaker’s site and then sell the produced steam to the offtaker under a long-term HaaS contract.

The primary benefit of a HaaS partnership is that the ESCO finances the upfront costs of the renewable thermal project, alleviating financial burden on the heat user. Additionally, the long-term nature of the contract offers industrial heat users predictable costs and can often insulate them from volatile energy pricing. This may increase cost efficiency and operational flexibility while decreasing offtaker reliance on fossil fuels.
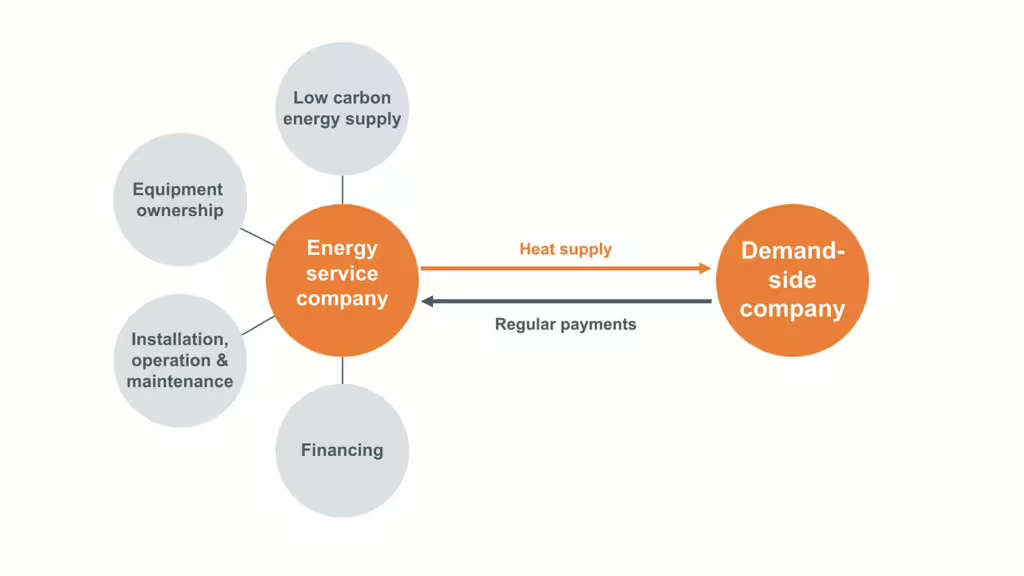
While long-term contracts can be an obstacle for industrial offtakers, the rate of HaaS adoption in industry is growing. The model’s growing popularity is driven in part by corporate aspirations to achieve sustainability goals, a shifting offtaker preference towards service-based heat structures rather than complete asset acquisition, and a desire to simplify complex stakeholder interactions. HaaS providers often manage relationships between engineering, procurement, and construction (EPC) firms, utilities, energy traders, and other parties who may play a role in implementing renewable thermal solutions. In most models, ESCOs manage all of these transactions, alleviating administrative and technical burden on heat offtakers.
What is the RTC doing?
The RTC creates resources and convenes its Members and Solutions Providers to help companies better understand HaaS and other financing opportunities across a variety of heat decarbonization technologies. The RTC also publishes knowledge products and case studies publicly to help industrial end users understand and evaluate financing options. These resources help increase large thermal energy users’ knowledge and awareness of financing opportunities used to implement solutions that can decarbonize their thermal applications.
Selected materials and webinars
RTC Case Studies
The RTC publishes case studies showcasing successful outcomes from the use of renewable thermal technologies. Many of these case studies feature use of HaaS models across a variety of technologies, including solar thermal, thermal energy storage, and electrification.
RTC case studies featuring use of HaaS financing include:
Heat as a Service: How to Decarbonize Commercial and Industrial Heat Use with Third-Party Capital Investments
This guide by the World Business Council on Sustainable Development (WBCSD) provides commercial and industrial companies with an introduction to HaaS. It explains the benefits and critical role of HaaS, identifies when HaaS is likely to be a particularly suitable solution, outlines key commercial considerations, and explains how to efficiently develop HaaS solutions.
How to get involved:
These work streams are developed with and informed by our Members and Solutions Providers. We regularly convene focused working groups to collaborate on this work. To join us in driving forward renewable thermal technologies, become a Member or Solutions Provider of the RTC. Existing Members and Solutions Providers may join this workstream at any point.
Contact:
Bailey Rosen, DGA: bailey@dgardiner.com




